[ad_1]
Due to Danny and Joe for evaluate.
Because the launch of the beacon chain grows nearer and eth2 turns into ever extra ultimate, the time has come to fast-sync the neighborhood with the newest on the internal workings of eth2 and on the concrete necessities, incentives and expertise of being a validator. This text will present a high-level overview of eth2 which can type the idea for a collection on all facets of eth2 related to validators.
eth2 has been within the works for a very long time now and has improved dramatically through the years. What have been initially separate sharding and Proof of Stake (PoS) efforts managed by way of good contracts has transmogrified right into a extremely interconnected design which yields dramatic enhancements concerning effectivity, scalability and safety.
The phases
As components of eth2 have grow to be extra interconnected, different items have been separated out into phases to permit for higher pipelining of the totally different facets of eth2. On the time of writing, Part 0 is nearing launch as builders put the ending touches on the consumer software program. In the meantime, the specification for Part 1 is being accomplished, and Part 2 is beneath energetic R&D.
- Part 0 is worried with the beacon chain, the core of eth2, which manages validators and the coordination of shards. The beacon chain is the supply of floor fact from which all different facets of eth2 are bootstrapped.
- Part 1 builds upon this by permitting information to be put into shards. The implementation complexity of this part is way smaller than the others as section 0 lays many of the floor work for the shards.
- Part 2 provides execution to eth2 principally upgrading eth2 from a strong database to a completely decentralised computing platform.
What precisely is Part 0?
As talked about beforehand, the beacon chain tracks the state of each the set of validators and the shards. In follow which means that should you (periodically) observe what is going on on the beacon chain, you’ll know sufficient to confirm something stated to be taking place inside eth2. Belief, however confirm.
To ensure that a PoS system to operate, there must be consensus on who the validators are, and on what every of their stakes are in an effort to understand how a lot their votes are value, and to appropriately reward and/or punish them for his or her behaviour. The beacon chain additionally manages the sharding facets of eth2 by assigning validator duties within the shards in addition to monitoring the present state of every shard.
A part of what differentiates eth2 from different PoS methods is the sheer variety of validators that may take part within the protocol. In distinction to the 10s, 100s, and 1000s of individuals which might be doable in different methods, eth2 scales to tons of of hundreds and even hundreds of thousands of validators. This stage of decentralisation is simply doable as a result of intermediate ranges of consensus achieved by teams of validators referred to as committees. The beacon chain makes use of the eponymous random beacon at its core to assign validators to committees that are tasked with evaluating what’s and is not part of the beacon and shard chains. A committee’s votes are then cryptographically aggregated into an attestation that means that verifying a whole committee’s votes is simply marginally extra effort than checking a single vote. Due to this fact, to test the validity of the beacon chain, just a few aggregated signatures must be thought of to guage the votes of many validators.
The beacon chain additionally tracks the eth1 chain and the deposits thereupon in order that new validators can be part of eth2 by sending 32 Ether to the deposit contract on eth1. On account of the beacon chain voting on the eth1 chain, eth2 will, sooner or later sooner or later, improve the safety of eth1 by offering an financial assure that blocks which might be part of the canonical eth1 chain.
Nodes vs. Purchasers
eth2 makes the excellence between beacon nodes and validator purchasers, and validators will want each in an effort to carry out their duties. A beacon node (or simply node) considerations itself with sustaining a view of the beacon chain in addition to whichever shards could also be wanted by a consumer or validator.
As their identify suggests, validator purchasers (or simply purchasers) deal with the logic of a single validator. That is achieved by speaking with the beacon node to grasp the present state of the chain, by testifying to and proposing blocks as properly when applicable, and at last by asking the beacon node to ship this info on to its friends.
If you’re not operating a validator, a beacon node accommodates the entire info it’s essential trustlessly work together with eth2, very like a full node in eth1.
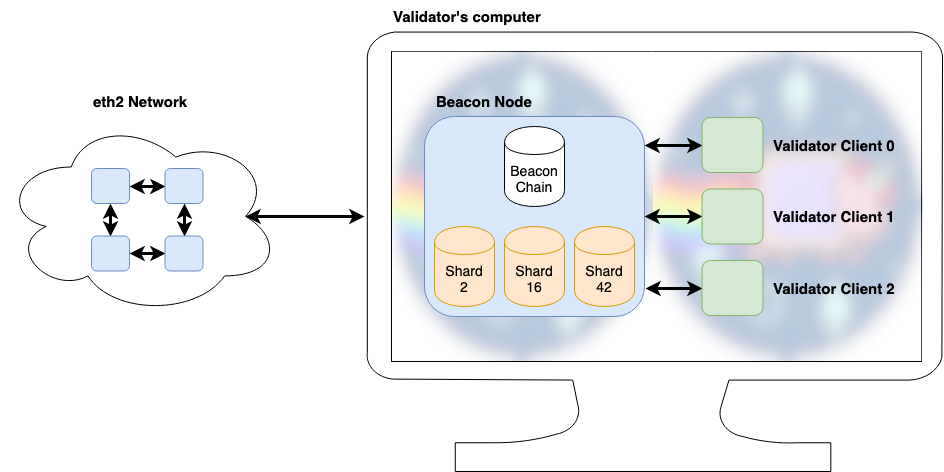
Under are among the many arguments for this separation:
- Every validator must be initiated with a deposit of precisely 32 Ether and due to this fact individuals who want to stake extra ETH might want to run a number of validator situations. The node-client separation permits such customers to solely run a single beacon node with a number of validators linked to it thereby lowering computation, reminiscence, and storage necessities.
- By having validator nodes be separate modules, they may possible be safer as it’s simpler to put in writing, cause about, and audit smaller code modules.
- For customers notably fearful about redundancy, a number of nodes could be run in parallel, thus lowering the possibility of a validator going offline.
- As a result of validator purchasers can solely work together with the remainder of the eth2 community by way of a beacon node, and even then by way of a restricted API, the assault floor of a validator node is significantly lowered.
- For customers who want to work together with eth2, however do not need to be a validator, they want solely function a beacon node which can grant them entry to the beacon chain and all of the shards they require.
Design Philosophy
The design philosophy of eth2 gives helpful context for all the choices made inside eth2 and in lots of situations encapsulate the variations between eth2 and different protocols.
- Protocol über alles: With the acknowledgement that the whole lot is a commerce off, the protocol’s security and liveness take priority over different design desiderata.
- Hope for one of the best, however anticipate the worst: eth2 assumes validators will likely be lazy, take bribes, and that they may attempt to assault the system until they’re in any other case incentivised to not. Moreover, the community is assumed to not be fully dependable and that catastrophic occasions might drive massive numbers of validators to go offline. For these causes, eth2 needs to be able to surviving World Conflict 3.
- Minimally viable complexity: Wherever doable, eth2 has been simplified as this makes it simpler to cause about, clarify to others, audit, write bug free purchasers, and customarily keep away from edge circumstances.
- Maximally decentralised: Proof of stake protocols generally compromise on the variety of validators that may take part, eth2 is designed to scale to hundreds of thousands of validators whereas encouraging these validators to work independently of each other.
- Count on the sudden: All elements of eth2 are proof against quantum computer systems or could be swapped out for these which might be within the occasion of a quantum apocalypse.
- By the individuals for the individuals: eth2 should be capable of run on a client laptop computer. The decrease the barrier to entry, the extra individuals who can take part which interprets into the next diploma of decentralisation.
Wrapping up
Now that you’ve the fundamentals of eth2 beneath your belt, the subsequent posts on this collection will deal with the juicy particulars of what makes eth2 tick.
[ad_2]
Source link




